

A positive z-score means that your x-value is greater than the mean.A z-score is a standard score that tells you how many standard deviations away from the mean an individual value ( x) lies: While data points are referred to as x in a normal distribution, they are called z or z-scores in the z-distribution. This allows you to easily calculate the probability of certain values occurring in your distribution, or to compare data sets with different means and standard deviations. When you standardize a normal distribution, the mean becomes 0 and the standard deviation becomes 1. Position or shape (relative to standard normal distribution) A small standard deviation results in a narrow curve, while a large standard deviation leads to a wide curve. The standard deviation stretches or squeezes the curve. Increasing the mean moves the curve right, while decreasing it moves the curve left. The mean determines where the curve is centered.
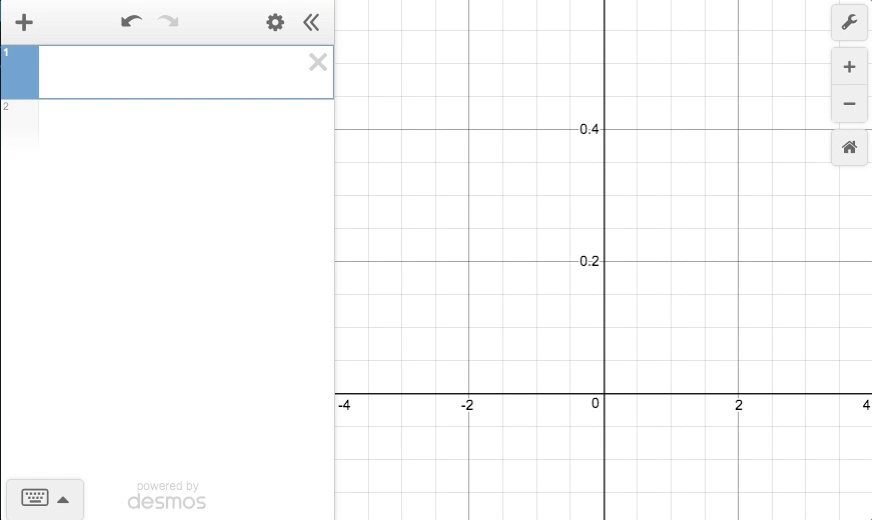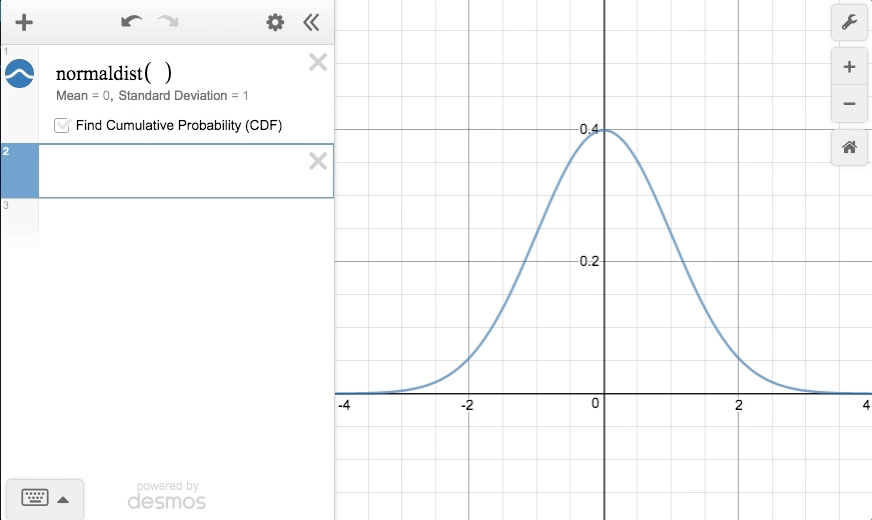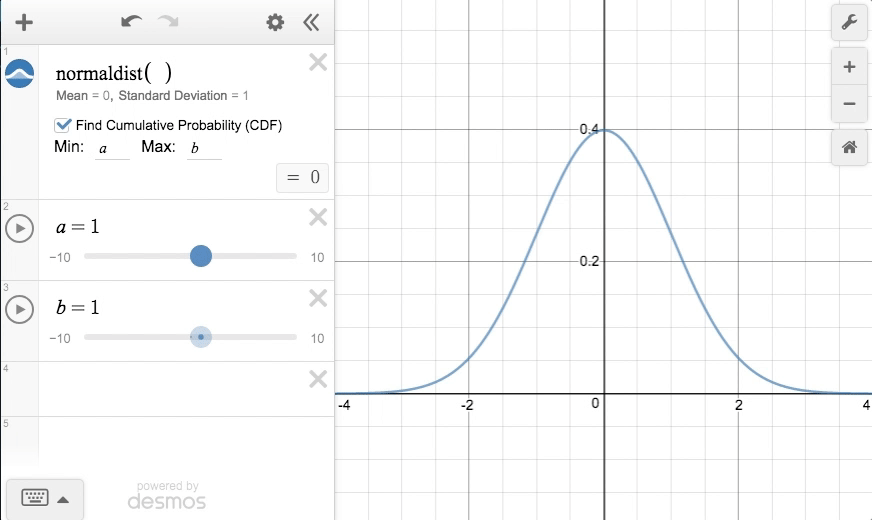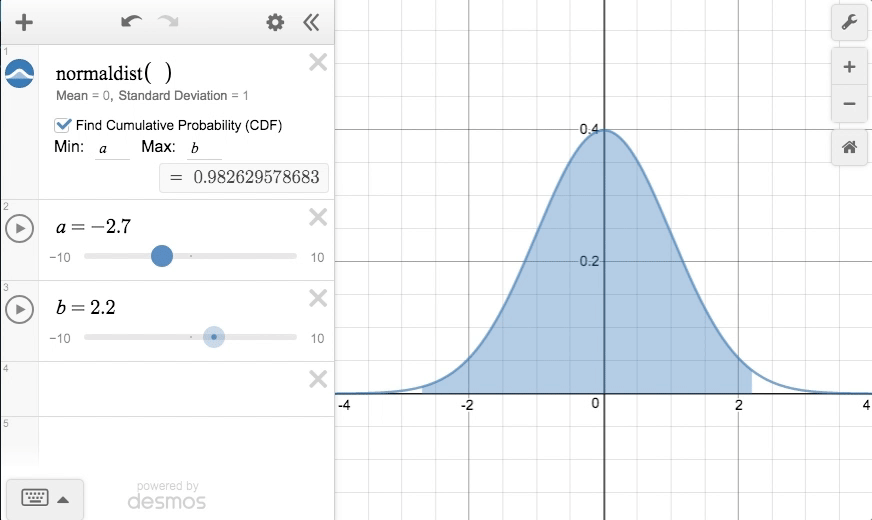
In the standard normal distribution, the mean and standard deviation are always fixed.Įvery normal distribution is a version of the standard normal distribution that’s been stretched or squeezed and moved horizontally right or left. However, a normal distribution can take on any value as its mean and standard deviation. Normal distribution vs the standard normal distributionĪll normal distributions, like the standard normal distribution, are unimodal and symmetrically distributed with a bell-shaped curve. Frequently asked questions about the standard normal distribution.Step-by-step example of using the z-distribution.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
